The three Pyramids of Giza, those of Cheops, Chephren and Mycerinus belong to the IVth. dynasty (2723 – 2563 BC) they represent the highest achievement in Pyramid construction. In fact, from Abu Rawoash (in the north) to the Fayoum (in the south) 100 KM (62 miles), totaling more than sixty in all. Their form may vary as well as their height and their technical character; some are unfinished, others are in an excellent state, or even partly demolished.
All the Pyramids are on the left bank of the Nile. near to the border between the cultivated land and the desert, or rather the lower or valley temple is found there at the beginning of the desert and the kingdom of the dead. At the end of the causeway, the upper temple or actual funerary temple is built. It is constructed on the east side of the Pyramid, although the pyramid entrance is generally found in the north. The question of orientation was important from the Egyptian point of view. Although there was no systematic and obligatory layout, a change of direction is often observed, after entering the north entrance, in the interior of the pyramid: at the east (Left) the chamber destined for the statue of the deceased is found (Serdab), whereas on the right, the West, is the sarcophagus chamber; therefore, the east signifies rebirth, whereas the west corresponds to the empire of the Dead. It is well-known fact that all the Old Kingdom pyramids are oriented on the four cardinal points by their faces, and with very great precision: so that the Cheops pyramid only differs bu 5° 30′ at the most from an absolute orientation; that of Chephren by 5° 32′ at the most and that of Mycerinus bu 14° 30′.
Significance and Meaning
The significance and meaning of the construction of the pyramids is uniquely sacred and religious. The dead king had to continue to exist in the afterlife because he became divine (in part) and also had to assure the welfare and survival of his people. Death was not the only important feature in prosaic reality (the pyramid, a giant simple tumulus to commemorate the memory of the dead one), the whole Egyptian mythological image counted almost as much because the two were intimately connected. That is the reason why the Old kingdom pyramids (the most important) were not constructed, as related in a very old legend, by hordes of humiliated salves but, a little like western cathedrals were built by organized groups of Egyptian peasants participating in a sacred operation. No doubt, the hardships of the work did, however, cause human suffering. That is the reason why this “Fatigue” was only practical during the time on inundation when fieldwork was stopped (and when the water came up to the desert and allowed the transportation of the blocks of stone almost to the place of work. When it is realized that almost 100,000 men worked for twenty years on the construction of Cheops’ pyramid, the exceptional system of provisioning, which must have been put in motion for such an army of workers and which allowed the porterage of water, food, materials, and necessary tools so that the planned program for Cheops could be finished in time, must be admired.
Almost 2½ million blocks of limestone, 2½ tons (each block more than a cubic meter) were piled up, several monoliths in the interior weigh more than 200 tons. The lower courses can reach 1.5 m (5ft.) in height, the upper courses are only 50 to 60 cm. (1ft. 8in – 2ft.) 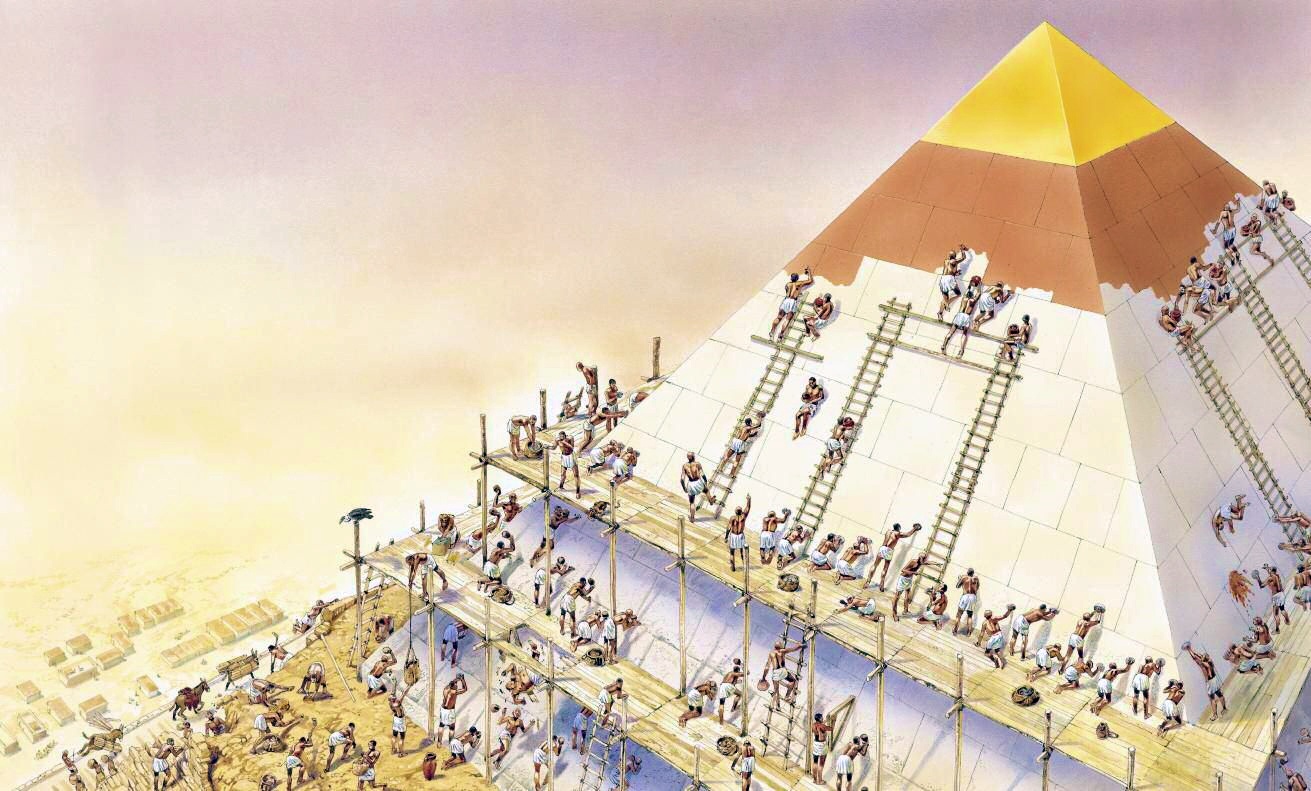 Tools and Means Used:
Tools and Means Used:
The diorite pounders, quartzite for polishing, the flint drills, the copper axes, and saws and the ramps of baked bricks on which the wooden sledges puled by men or beasts were slid, formed the principal means employed in constructions, because the wheel, lever, block and tackle, and iron tools were as yet unknown. Nevertheless, the construction was so precise in certain cases that the level of the courses for a length of 200 m (636 ft.) doesn’t vary more than 2 cm. (1 in.)
Organization of the Work:
First of all, the rock platform was leveled then the first layer was set down, the lower layer which formed a square stone foundation Then a brick or mud ramp was installed on which it was possible to up the necessary material to the second layer well as the blocks themselves (on wooden sledges). The ramp was built up and lengthened for the third course and the following courses so that the ramps become progressively longer and higher. The necessary interstices for corridors and chambers were evidently arranged according to the architect’s plans. Finally when the Apex was reached. the courses had the appearance of an immense staircase (something like their present state). then, going from top to bottom, the already conveniently cut casing blocks were added, which were finally carefully polished, course by course, so that the ramps were simultaneously demolished. The immense mass of material must have been used merely for the construction of the ramps, of which nothing remains today, can be imagined.
The building material:
The building material used for the body of the pyramids was chiefly lime0stone found at the site, although for casting blocks, the fine, white nummulitic limestone from the quarries of Tura facing Memphis was used (making the maximum use of the Nile in flood). The greater part f the casting blocks were removed in the Middle Ages and re-used as cheap building, material in the Citadel and monuments of Cairo, but there is a little remaining on the three pyramids.






One more thing. It’s my opinion that there are several travel insurance web sites of respected companies that allow you to enter your holiday details and have you the quotes. You can also purchase this international holiday insurance policy online by using the credit card. All you should do is to enter your travel details and you can understand the plans side-by-side. Merely find the package that suits your financial allowance and needs after which use your credit card to buy the item. Travel insurance on the web is a good way to do investigation for a dependable company pertaining to international travel cover. Thanks for expressing your ideas.